Most WiFi routers have a range of about 100 to 150 feet, but there are many factors that can impact your signal quality. If you’re finding that your WiFi signal is slow or sluggish in certain areas of your home, here are a few simple ways to boost your WiFi signal.
Step 1: Identify Any Interfering Appliances
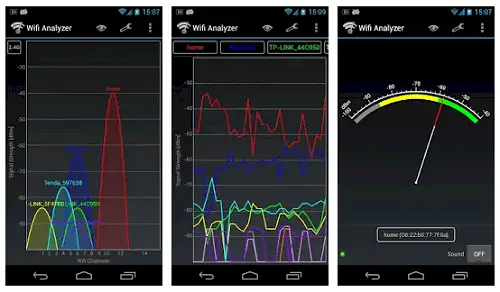
Screenshot via Google Play
Use your wireless network analyzer to identify other household appliances that may be interfering with your WiFi signal. Common interfering appliances include:
- Microwave ovens
- Cordless phones
- Security alarms
- Remote controls (garage door openers, television remotes, etc.)
- Baby monitors
Helpful Tip: Compare your router’s signal strength with each appliance on and off to identify the appliances that are interfering with your WiFi signal. Network Analyzer Lite works with iOS devices. For Android devices, Wifi Analyzer is an option. Or, go big with the AirMagnet WiFi Analyzer PRO.
Step 2: Move Your Wireless Router to a Better Location

Now that you know what appliances are interfering with your signal, it’s time to relocate your router to a better location. Routers are best placed in the open, where the signal doesn’t have to travel through walls and other obstructions like large cabinets or furniture. Keep it away from appliances and metal objects.
Helpful Tip: Place your router near the center of your home to get the best possible signal in every room. Locate your router on the top floor if possible, as radio waves travel most efficiently down and laterally.
Step 3: Adjust Your Router’s Antennas

It seems too easy, but often, simply adjusting your router’s antennas can offer a signal boost. If you use both laptops and desktops, you’ll find that positioning the antennas perpendicular to each other offers a better signal. Why? Router antennas work best when oriented the same way as the device’s antenna, and in laptops, that’s horizontal, but in desktops, they’re vertical.
Step 4: Hack Your Antennas

Screenshot via Amazon
If your router has a built-in antenna, adding an external antenna can make a big difference in signal strength. You’ll need to purchase one compatible with your router, but most manufacturers sell both omnidirectional and directional external antennas. Directional is best, as you can point the antenna in the direction where your signal is weakest to get the biggest gains. If your router has a twist-off antennae with RP-SMA connectors, get some RP-SMA antenna extension cables to boost your signal.
Keep in Mind: Most built-in antennas are omnidirectional. If you’re adding an external antenna, choose one labeled “high-gain.”
Helpful Tip: If you’re the DIY type, you can use a tinfoil hack, an aluminum can, or even a mesh colander for a similar effect.
Step 5: Update Your Router’s Firmware
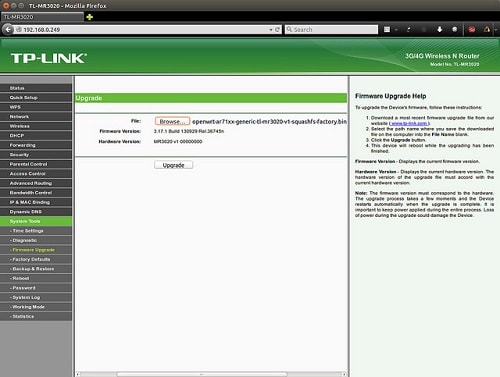
Image via Flickr by Gareth Halfacree
Yes, routers have firmware updates, too, and those updates often include performance enhancements, new features, and perhaps most importantly, security updates. If your router is newer, updating the firmware is usually as simple as logging in to the administrator interface and clicking an “Update Firmware” button.
Keep In Mind: If you have an older router, you may need to find and download firmware updates from your router’s manufacturer’s website first. Most current routers have this process built-in to the administrator interface – and this convenience alone may make it worthwhile to invest in a newer router.
Step 6: Change Your Router’s Channel
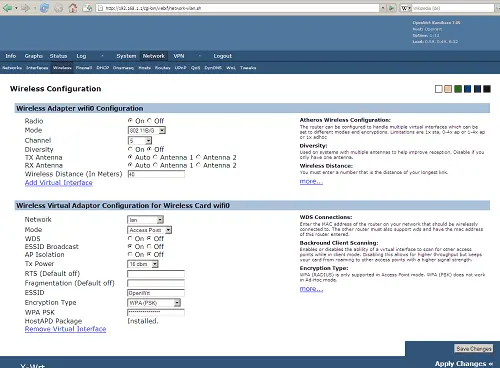
Image via Wikimedia Commons
Wireless routers can operate on a number of channels. From a Windows PC, go to the command prompt and type netsh wlan show all to see a list of all wireless networks and channels in use in your vicinity. Go to your wireless network’s administrator interface and change your router’s channel to one that is less commonly used. The administrator interface may vary depending on your device and wireless service provider, but this setting is typically found in the basic wireless settings.
Step 7: Change Your Frequency
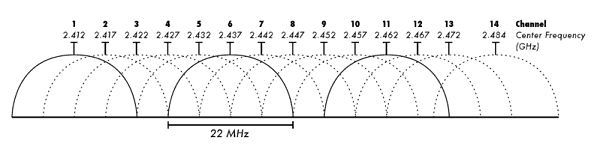
Image via Wikimedia Commons
Your router operates on a frequency, most commonly the 2.4GHz band. If you have a dual-band router, however, you have the option of switching to the 5.0GHz band, which can offer better performance and throughput. Go to your network’s administrator interface to see if your router offers 5.0GHz as an option, and if so, enable it.
Step 8: Prioritize Apps and Services with Quality-of-Service Tools
Image via Wikipedia
Most routers come with Quality-of-Service (QoS) tools that allow you to specify which applications and services get priority bandwidth allocation. Use these settings to cut down on sluggishness that results from multiple people using the same network at the same time. For instance, you can prioritize videos and phone calls so that they don’t cut out when someone else is downloading a large file from the web. Go to advanced settings in your network administrator’s interface to find QoS tools.
Step 9: Install a Repeater or Wireless Bridge
Image via Amazon
If you’re still not getting a sufficient signal, install a WiFi repeater or wireless bridge. A repeater will extend your wireless signal without the need for a bunch of additional wires. Place it halfway between your wireless access point and your device. If you’re trying to get a better signal for wired devices, you’ll want a wireless bridge, also known as an ethernet adapter.
When all else fails, it may be time to invest in a new wireless router, particularly if your current model is a few years old. The newest routers allow you to adjust the aforementioned settings with ease, and they’re equipped with the most options as far as channels, frequency, and performance – so the investment is usually well worth it.






